 Threat Intel
Threat Intel
Fortiweb – CVE-2025-64446
Another day another exploit in the wild it seems! (ok I’m a bit slow to this one). Using Defused Cyber’s Honeypots we have another packet to analyse:
Read more “Fortiweb – CVE-2025-64446” Threat Intel
Threat Intel
Another day another exploit in the wild it seems! (ok I’m a bit slow to this one). Using Defused Cyber’s Honeypots we have another packet to analyse:
Read more “Fortiweb – CVE-2025-64446” → Leadership
Leadership
Ok a bit dramatic, but that’s often what you might feel if you spend lots of time in the vulnerability space (which if you work in cyber security.. you probably do!). We often hear about the NEXT: STUXNET, HEARTBLEED, WANNACRY/ETERNAL BLUE, LOG4J etc. but actually when it comes to it… the number of times we have word endangering unauthenticated remote code execution that is a danger to global society is far less than when we have other vulnerabilities. It’s the exception not the rule.
Read more “OMG The Cyber SKY is falling down!” → Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities
Regarding: CVE-2023-23397
This is a fast publish, use at own risk.
See guidance from Microsoft: CVE-2023-23397 – Security Update Guide – Microsoft – Microsoft Outlook Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
If you need to mitigate the latest Outlook vulnerability which abuses an SMB/WebDav call using the Calendar invite feature you can consider the following:
Read more “Microsoft Outlook Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability (CVE-2023-23397)” → Education
Education
Some friends and I did some testing this evening with TOX clients. We wanted to take a look at PERSEC/OPSEC considerations for using TOX. I also had a sneaky suspicion that it might out of the box leak more than people would appreciate (just a hunch and you don’t know until you test right!).
So, we setup a test. In the test we had:
Read more “Some TOX Clients Leak Egress IP addresses” → Threat Intel
Threat Intel
https://www.icann.org/resources/pages/dnssec-what-is-it-why-important-2019-03-05-en
Ok read all that good. What we are talking about here is signing a DNS zone to “assure” that the client is getting DNS responses from the right ZONE data. DNSSEC does not encrypt the conversation between DNS client and DNS server. It does enable the client to be able to check if the data it gets back is valid. In short what we are doing is validating that the “data” being returned is authorized and not tampered with.
Read more “DNSSEC – why not having a signed zone is almost never going to lead to you getting pwn3d” → Threat Intel
Threat Intel
Adversary: Unknown, likely Criminal Actor/s
Initial Access Vector: Unknown/Unproven
Impact: ~3K+ Hosts have had Remote Code Execute and their ESXi logon pages changed (plus had encryption routines run to encrypt virtual machines, with varying success). A Second encryption routine has been deployed to some hosts; the threat actor is expanding/changing capabilities.
Risk: Further impact, Additional Threat Actors Exploit the vulnerability
Read more “ESXiargs Summary 09-02-2023 10:03” → Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities
The latest guidance from Microsoft (released on the 02/10/2022) says to disable administrators from being able to execute remote PowerShell via the exchange PowerShell web endpoint /PowerShell

October 2, 2022 updates:
Obviously bear in mind this needs auth! but also auth isn’t always that hard..
Microsoft Research have just released (0825 30/09/2022) this: Customer Guidance for Reported Zero-day Vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange Server – Microsoft Security Response Center
Microsoft have released a Exchange Server Emergency Mitigation (EMS) which includes URL re-write rules to HELP mitigate this (but likely don’t eliminate all risks due to potential bypasses)
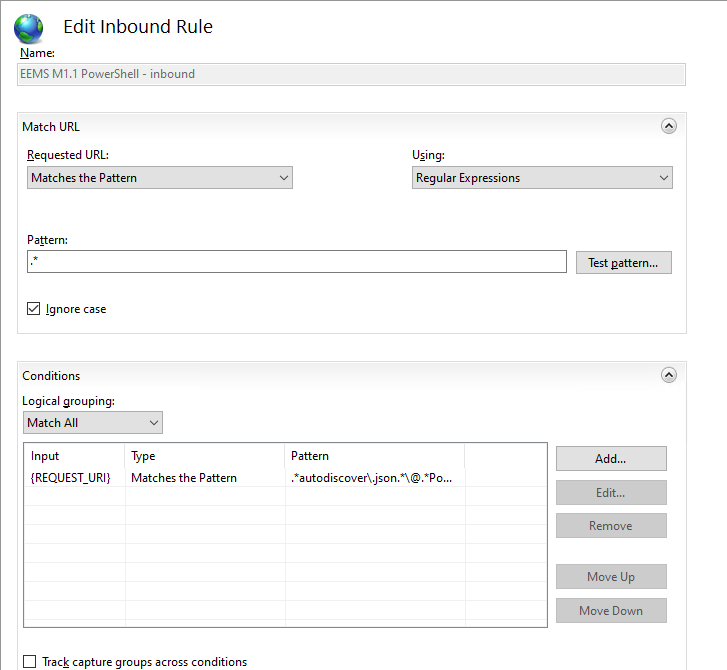
Likely “Zero day” exploit in the wild being used to attack exchange servers via a simmilar endpoint to ProxyShell. A mitigation is to apply URL rewrite rules, or to disconect the service internet from untrsuted networks until a patch is available. The Exploit is reported to required AUTHENTICATION, which may significantly limit the volume of exploitation (however credentials are only a phish away). It’s also reported the exploitation in the wild used /Powershell after exploiting the autodiscover endpoint.
Yesterday it was reported there was a “new” zero day vulnerability being exploited in the wild. But there appears to be some confusion and a lack of speciifc evidence to showcase the vulnerability being “new” or simply being a differnt exploit path/approach for an existing CVE (e.g. ProxyShell).
The situation from my pov (at time of writing) is still unclear. It would be odd to not advise people ensure they are running the latest supported Exchange CU and Security update release (check both!) – if the exploits are 0-day (which it looks like they are) you will need to also patch when MS release a patch!
New Microsoft Exchange zero-days actively exploited in attacks (bleepingcomputer.com)
Upcoming | Zero Day Initiative
Upcoming | Zero Day Initiative
Read more: Exploitation of Microsoft Exchange Servers seen in the wild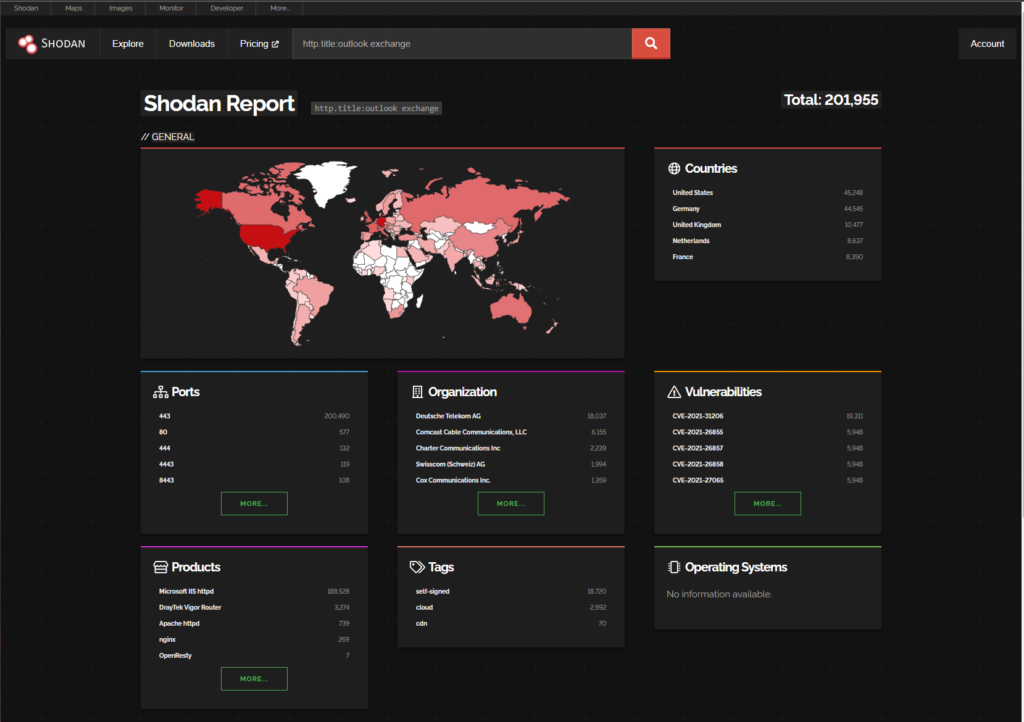
https://www.shodan.io/search/report?query=http.title%3Aoutlook+exchange
There are 201,995 Exchange Servers with Outlook Web Access Exposed (According to Shodan)
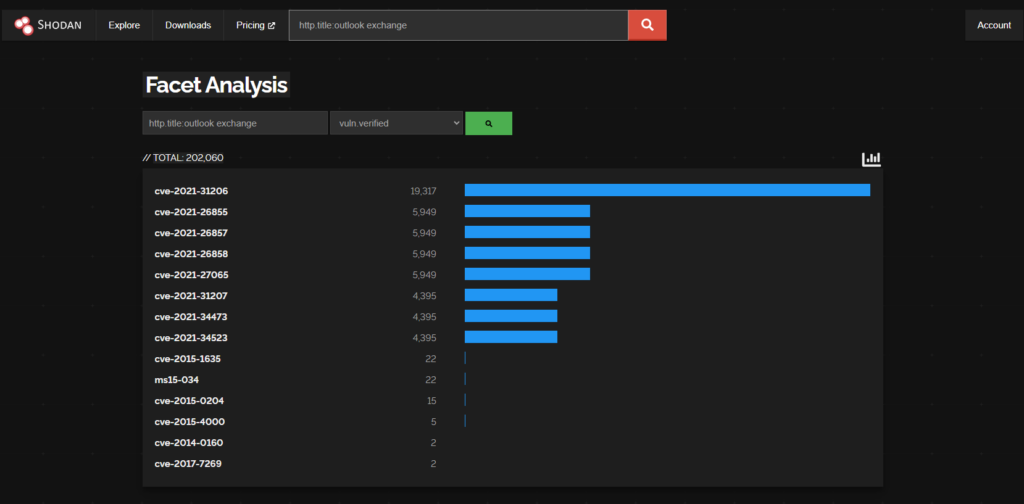
cve-2021-31206 (19,311)
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2021-31206
9.5% of the worlds Exchange attack surface is vulnerable to CVE-2021-31206
CVE-2021-34473 (4388)
CVE-2021-34523 (4388)
CVE-2021-31207 (4388)
2.1% of the worlds Exchange attack surface is vulnerable to ProxyShell CVEs (above) (based on the shodan data)
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/new-features/updates?view=exchserver-2019
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/new-features/updates?view=exchserver-2019
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/confirmation.aspx?id=58392
The situation appears to be evolving, as always security vulnerabilities and in the wild exploitations can be a fast moving landscape, internet facing systems need suitable and adequate protections, that doesn’t include just exposing IIS on TCP 443 and walking away. It requires capabilities such as:
and many more things!
This post is a fast publish and may contain errors and/or the situation may change. I’ll try and keep it updated.
 Defence
Defence
Working out what exploits to care about is a tough job, kill chains, availability of exploits, complexity, data flows, controls etc. all play a part in understanding a vulnerability and how it affects your organisational risk. To support this effort I’ve started to compile a list of public exploits against CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV). This may be useful for defensive and offensive security pros.
Read more “Offensive KEV Alpha 0.1” → Hacking
Hacking
When you gain access to a target node you will want to explore, the exact method you use to do this will depend upon operational security considerations, time constraints and style. You will be looking for a range of elements to support progressing an objective.
It should be noted that the objective may NOT require elevation. You may be trying to obtain data and access might already be possible using the context you have assumed.
You also may need to move from a www-data user to a named user account or get to root level of access. If so there’s a range of questions we should be asking ourselves:
Read more “Linux Privilege Escalation” → Defence
Defence
Spotted on twitter (thanks Danny!):
already ahead of u 😉 you know that all the infosec pros have to read every one…. well ones relvent to their environment/scope…. 😛 x pic.twitter.com/AnMqiLjNvB
— MrR3b00t | #StandWithUkraine #DefendAsOne (@UK_Daniel_Card) June 9, 2022
CISA updates the known exploited vulnerabilities list (KEV) yesterday with another 38 updates!
That means an update is required for OFFESNIVE KEV!
Read more “Offensive KEV Updates! CISA releases 38 more CVEs to KEV” →